Long-term debt is also known as bonds payable and it’s usually the largest liability and at the top of the list. The most common liabilities are usually the largest such as accounts payable and bonds payable. Most companies will have these two-line items on their balance sheets because they’re part of ongoing current and long-term operations. The effective interest rate of the investment in the debt security is approximately 7.65%.
Contractual cash flow characteristics (‘SPPI test’)
When the company pays its balance due to suppliers, it debits accounts payable and credits cash for $10 million. When a company determines that it received an economic benefit that must be paid within a year, it must immediately record a credit entry for a current liability. Depending on the nature of the received benefit, the company’s accountants classify it as either an asset or expense, which will receive the debit entry. Companies acquire trading assets with the purpose of trading them for a profit. When a company buys and sells a trading asset, it is marked at the fair value of the asset. When trading assets are held by banks for other banks, they are valued at mark-to-market.

Finalized rule adopts modified June 2018 proposed Amendments
- In this alternative model, the entity continuously reinvests in new short-term assets until the need for capital arises, primarily focusing on holding assets to collect contractual cash flows, with only minor sales before maturity.
- The 2013 Rule contains various exclusions and exemptions from the scope of prohibited proprietary trading.
- IFRS 9 further elaborates that ‘held for trading’ usually indicates active and frequent buying and selling.
- Financial assets that are held for trading are always classified as financial assets at fair value through profit or loss.
Bank XYZ would hold its trading assets in an account separate from the long-term investment portfolio, hold them for a short period of time, and trade them as appropriate in the marketplace to make a profit for the bank. The key point to note is that trading assets are for the short term where the investment portfolio is typically geared toward the long term. The final rule also clarifies that if the banking entity or an affiliate sponsors or serves as the investment manager or adviser to a covered fund, then the banking entity or affiliate will be deemed for purposes of the marketing restriction to participate in any offer or sale of ownership interests in the covered fund. The final rule allows a banking entity to acquire a covered fund interest as a hedge when acting as an intermediary on behalf of a customer that is not itself a banking entity to facilitate the exposure by the customer to the profits and losses of the covered fund, so long as the activity is designed to mitigate risk.
Underwriting and Market Making for Third-Party Covered Funds
For assets or liabilities that are not quoted in an active market, fair value is determined using valuation techniques, such as discounted cash flow models or option-pricing models. An entity must apply the effective interest rate method in the measurement of amortised cost. The effective interest rate method also determines how much interest income or interest expense should be reported in profit and loss. IFRS 7 deals with financial instruments’ disclosures and pulls them together in a new standard. The following decision tree summarises the classification of financial assets according to IFRS 9.
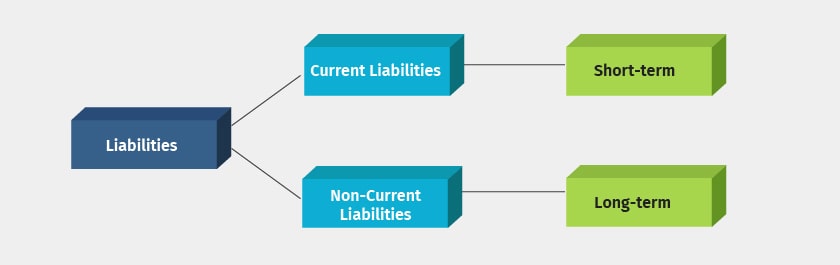
Liability: Definition, Types, Example, and Assets vs. Liabilities
Other companies may hold trading assets in order to hedge positions naturally related to their core operations. For instance, an oil producer may sell oil futures while an airline may purchase oil futures, both not wanting to be exposed to market risk in the price of oil. It’s a long-term liability if a business takes out a mortgage that’s payable over a 15-year period but the mortgage payments that are due during the current year are the current portion of long-term debt. The final rule also eliminates the requirement that no financing be provided by any branch or affiliate located in the United States or organized under the laws of the United States or of any state for a banking entity’s ownership or sponsorship of a covered fund in reliance on the SOTUS exemption.
Financial assets at fair value through profit or loss are re-measured to fair value at each subsequent balance sheet date until the assets are de-recognised. The gains and losses arising from changes in fair value are included in the income statement in the period in which they occur. Gains and losses will include both realised gains and losses arising on the disposal of these financial assets and unrealised gains and losses arising from changes in the fair value of the assets still held.
This option to designate financial liabilities to be measured at FVTPL applies when an entity manages a group of financial liabilities or financial assets and financial liabilities in a manner that results in more relevant information if the group is measured at FVTPL. The emphasis here is on how the entity manages and evaluates performance, rather than the nature of its financial instruments (IFRS 9.B4.1.33). Federal financial regulators responsible for implementing the Volcker Rule have issued a final rule to revise a number of provisions of the Volcker debit balance definition Rule’s 2013 implementing regulations (the “2013 Rule”). The final rule, which is largely similar to the agencies’ proposed rulemaking issued in June 2018, generally seeks to clarify certain definitions, exemptions and compliance requirements under the 2013 Rule, and to tailor compliance requirements to be commensurate with a banking entity’s level of trading activity. When a financial asset or financial liability is recognised initially in the balance sheet, the asset or liability is measured at fair value (plus transaction costs in some cases).
In order to be classified as held-to-maturity, a financial asset must also be quoted in an active market. This fact distinguishes held-to-maturity investments from loans and receivables. Loans and receivables, and financial assets that are held for trading, including derivatives, cannot be classified as held-to-maturity investments.
Due to falling market interest rates, the bond trades at $1,020, which is the amount Entity A pays for the bond (i.e., its fair value). A liability is anything you owe to another individual or an entity such as a lender or tax authority. The term can also refer to a legal obligation or an action you’re obligated to take. Companies of all sizes finance part of their ongoing long-term operations by issuing bonds that are essentially loans from each party that purchases the bonds.
